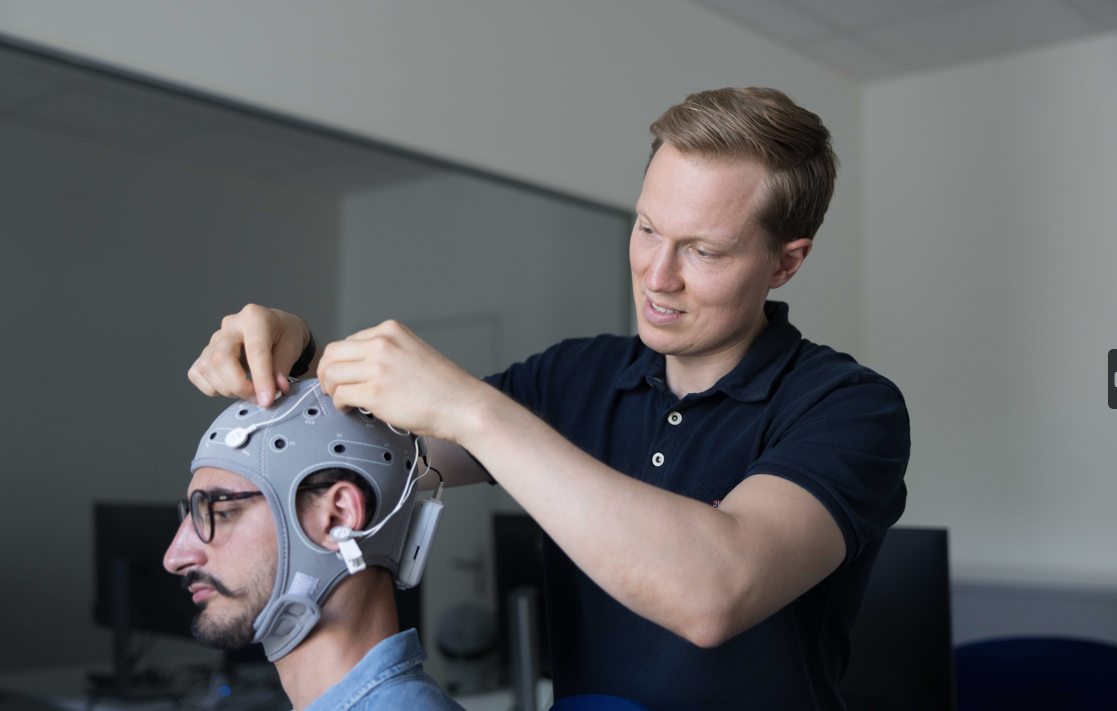


Unsere hochmoderne Hard- und Software sowie das erfahrene Laborteam ermöglichen es Ihnen, qualitativ hochwertige und effiziente Forschungsprojekte unter Anwendung neurophysiologischer Methoden durchzuführen.
Der neurophysiologische Teil des Labors verfügt über separate Mess- und Kontrollräume. Für klassische Experimente ohne neurophysiologische Beobachtungen haben wir ein PC-Labor mit 20 Arbeitsplätzen und einen Fokusgruppenraum.

Die Verwendung neurophysiologischer Messungen hat sich auf neue Forschungsbereiche ausgeweitet, da der Zugang zu Messgeräten und anderen Ressourcen erleichtert wurde. Durch die Verwendung neurophysiologischer Messungen allein oder in Synergie mit traditionellen Selbstauskünften können Forschende viele der typischen Verzerrungen überwinden, welche die Zuverlässigkeit ihrer Daten beeinträchtigt haben. Ursprünglich aus der Psychologie und der medizinischen Forschung stammend, werden die Instrumente und Methoden, die wir im neurophysiologischen Teil des Behavioral Labs unterstützen, heute in Spitzenpublikationen in allen für die Universität St. Gallen relevanten Disziplinen verwendet.
Für Beispiele an Top-Publikationen die neurophysiologische Forschungsmethoden verwenden, wenden Sie sich an behaviorlab@unisg.ch
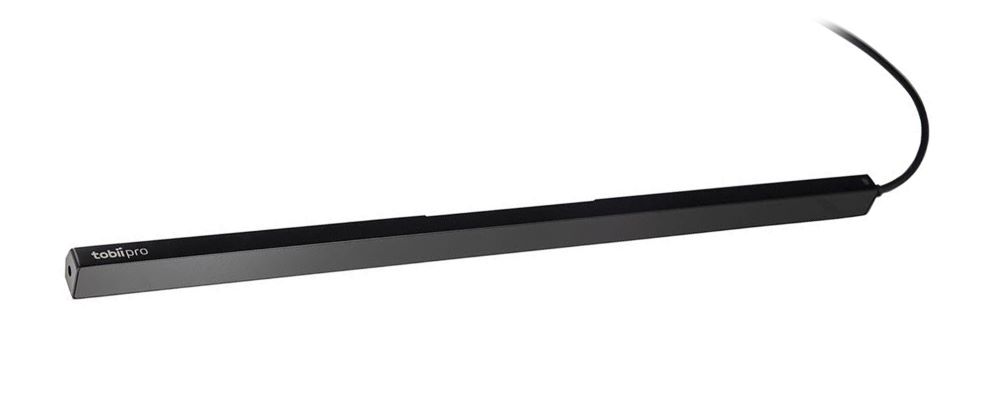
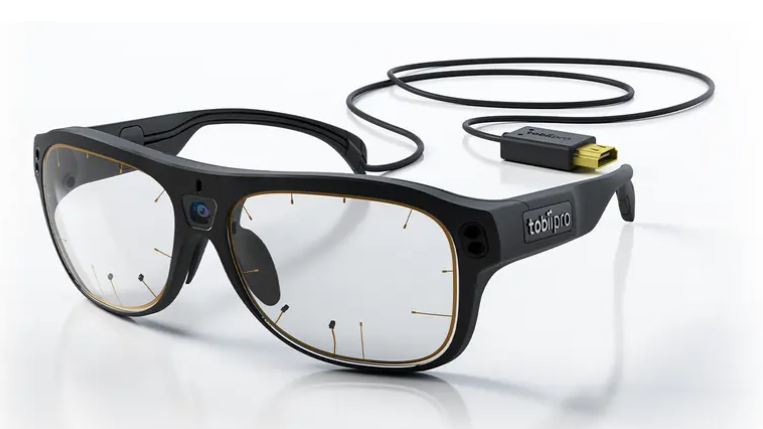


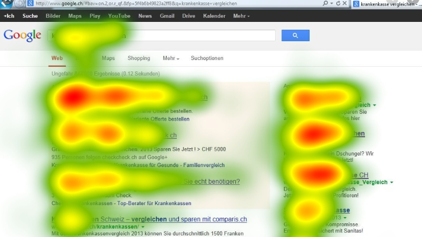
Die Eye-Tracking-Technologie misst die Position und Bewegung der Augen, was Aufschluss über Aufmerksamkeitsprozesse, den Vergleich von Gruppenverhalten, stimulusinduzierte visuelle Reaktionen und mehr geben kann. Infrarotkameras richten Licht auf die Pupillen der Teilnehmenden, wodurch Reflexionen entstehen, die die Bewegung und Richtung der Augen aufzeigen können.
Geräte:
Tobii Fusion 120Hz
Tobii-Brille 3
Varjo XR-3 (integriert mit VR/AR)
Software:
Analysen und Aufzeichnungen können sowohl in iMotions als auch in der Tobii ProLab Software durchgeführt werden.

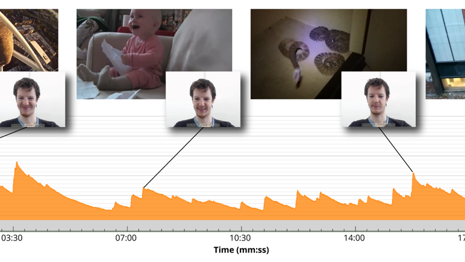
GSR, auch bekannt als elektrodermale Aktivität oder Hautleitfähigkeit, kann verwendet werden, um Erregung, Interesse, Engagement oder Stresspegel zu beobachten - Reaktionen, die sich unserer bewussten Kontrolle entziehen. Emotionale Stimulation löst die Schweissdrüsen in unseren Handflächen und Fusssohlen aus, die der GSR misst, um den Grad der Schweissbildung auf der Hautoberfläche anzuzeigen.
Gerät:
Schimmer3 GSR+
Software:
iMotions oder die eigene Shimmer-Software

Neben den medizinischen Anwendungen kann die Elektroenzephalographie (EEG) in einer Vielzahl von Forschungsbereichen eingesetzt werden, die für die Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler der Universität St. Gallen relevant sind. Durch die Beobachtung der elektrischen Aktivität des Gehirns von Probanden und Probandinnen können wir zuverlässige und objektive Daten über mentale Metriken wie Arbeitsbelastung, Engagement, Schläfrigkeit oder Wachsamkeit sammeln.
Die Ausrüstung, die wir derzeit haben:
Neuroelektrik Enobio 8
Emotiv Epoc X 14
Das drahtlose B-Alert X10 von Advanced Brain Monitoring
Software:
iMotions oder die eigene Emotiv/Enobio/ABM-Software
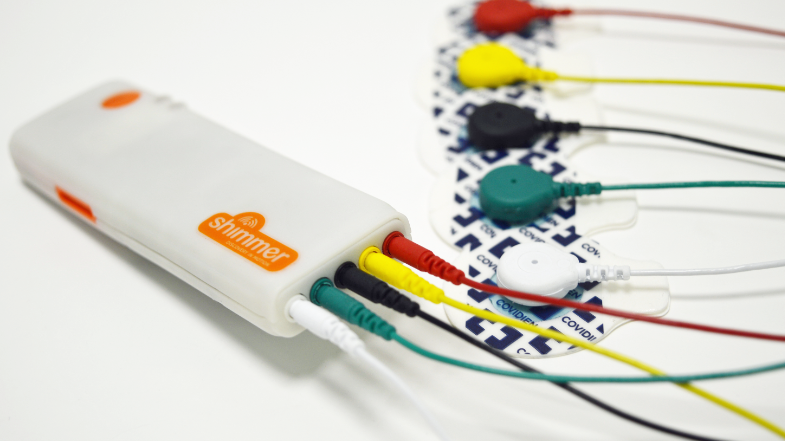

Die Elektrokardiographie (EKG) ermöglicht die nicht-invasive Messung der Herzfrequenz und der Herzfrequenzvariabilität und liefert wichtige Erkenntnisse über die Funktion des autonomen Nervensystems und das emotionale Engagement. Die Messung erfolgt auf nicht-invasive Weise, indem Elektroden auf der Haut in der Nähe des Herzens angebracht werden.
Geräte:
Shimmer3 EKG-Gerät
Software:
iMotions oder die eigene Shimmer-Software

FEA misst Emotionen anhand von Gesichtsausdrücken. Die Technologie verwendet eine Software, die Gesichtsmerkmale erkennt, Mikroausdrücke interpretiert und sie zu sieben Grundemotionen zusammenfasst: Freude, Wut, Überraschung, Angst, Verachtung, Traurigkeit und Ekel. Die Wertigkeit beschreibt die Gesamtstimmung.
Geräte:
Jede hochauflösende Webcam kann für FEA verwendet werden. Es ist auch möglich, zuvor aufgezeichnete Videos nachzubearbeiten.
Software:
Affectiva AFFDEX über iMotions

Das PC-Labor verfügt über 20 Computer mit Headsets und Kabinen, um Blickkontakt zu vermeiden. Es eignet sich für kontrollierte, computergestützte Experimente wie Multiplayer-Strategiespiele, Umfragen und Quizze sowie psychologische Experimente.
Geräte:
20 PCs mit Bildschirmen, Webcams, Mikrofonen und Kopfhörern
Software:
zTree - Softwarepaket zur Entwicklung und Durchführung von ökonomischen Experimenten (Client-Server-Anwendung)
oTree - Open-Source-Plattform für webbasierte interaktive Aufgaben (basierend auf Python)
E-Prime 3.0 - All-in-One-Plattform, die eine millisekundengenaue Zeitmessung ermöglicht, um die Genauigkeit der Daten zu gewährleisten.

Virtuelle Realität (VR) ermöglicht Verhaltenstests in jeder Umgebung. Forscher können Stimuli in VR/AR einrichten, um diese Umgebungen zu testen oder von realen Stimuli zu lernen, die zu komplex oder zu teuer sind, um sie mit anderen Methoden zu testen. Die meisten neurophysiologischen Messverfahren können in der VR/AR-Umgebung eingesetzt werden.
Geräte:
HTC Vive Pro
Varjo XR-3
Software:
iMotions (für die Integration von neurophysiologischen Messgeräten), Unity oder der eigenen HTC/Varjo-Software für die VR/AR-Umgebung.
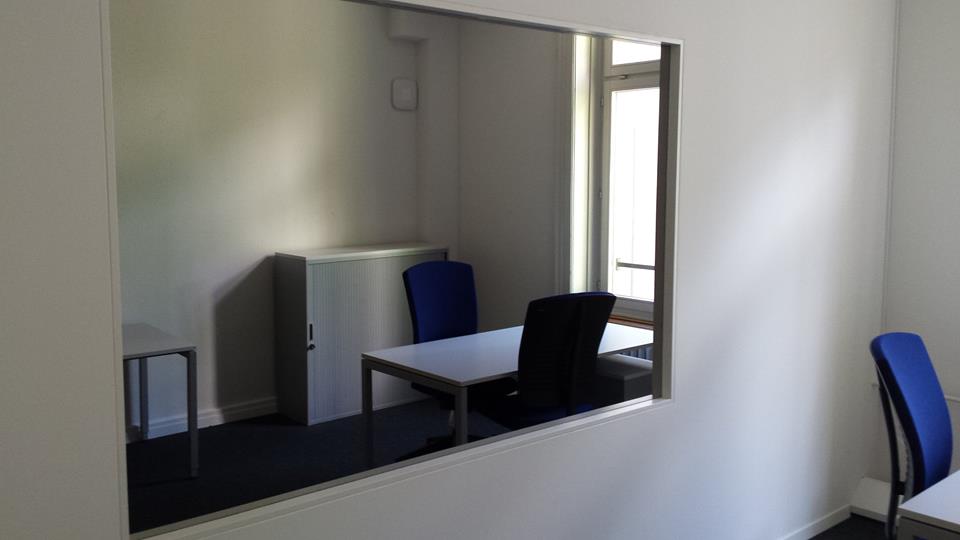

Dies ist ein Raum mit schalldichten Wänden und Decken, Kameras mit Mikrophon und einem einseitigen Spiegel, ideal für die Durchführung von Fokusgruppen, Interviews, Studien zum Verhalten der Teilnehmer und die Analyse von Teaminteraktionen.
Geräte:
Zweiseitiger Spiegel
Überwachungs-Kamera
Audioaufnahme