
Throughout the entire Bachelor's programme in Economics, you will be equipped with the necessary tools for economic careers and research in the digital age. The focus is on understanding global social and economic challenges, such as globalisation, financial crises, unemployment or pension provision.


In the Major Economics, we focus on a holistic education. Our graduates are prepared to take on leadership roles and social responsibility in a highly dynamic environment. Soft skills are developed through the University of St.Gallen’s Contextual Studies.
Graduates of the Major Economics develop five core competencies:
The curriculum of the Major Economics consists of three components: the Core studies (84 ECTS credits), the Contextual studies (24 ECTS credits). Completed is the degree with the Bachelor’s Thesis, including the Thesis Preparation Colloquium (12 ECTS credits). While the Core studies focus on developing students' expertise in economics, the Contextual studies are designed to enhance their social and cultural competencies.
The order of semesters in which you can take compulsory courses is only a recommendation and you can change it according to your needs. Especially when planning an exchange study, it may make sense to complete the courses in a different order.
The Assessment Year at the University of St.Gallen (HSG) is the first year of the Bachelor's programme, during which students acquire a broad foundation of knowledge in economics and law. The curriculum includes both Core studies and Contextual studies, amounting to a total of 60 ECTS credits. The Core studies include mandatory subjects such as Business Administration, Economics and Law. The required Electives, either Mathematics for Economics or Law for Law Studies, is determined by the chosen Major. The Contextual studies cover areas such as skills development, cultural and social sciences, and foreign languages. Throughout the year, students must complete various assessments, including written exams, seminar papers, group projects, oral exams, and presentations.
learn more about the Assessment Year
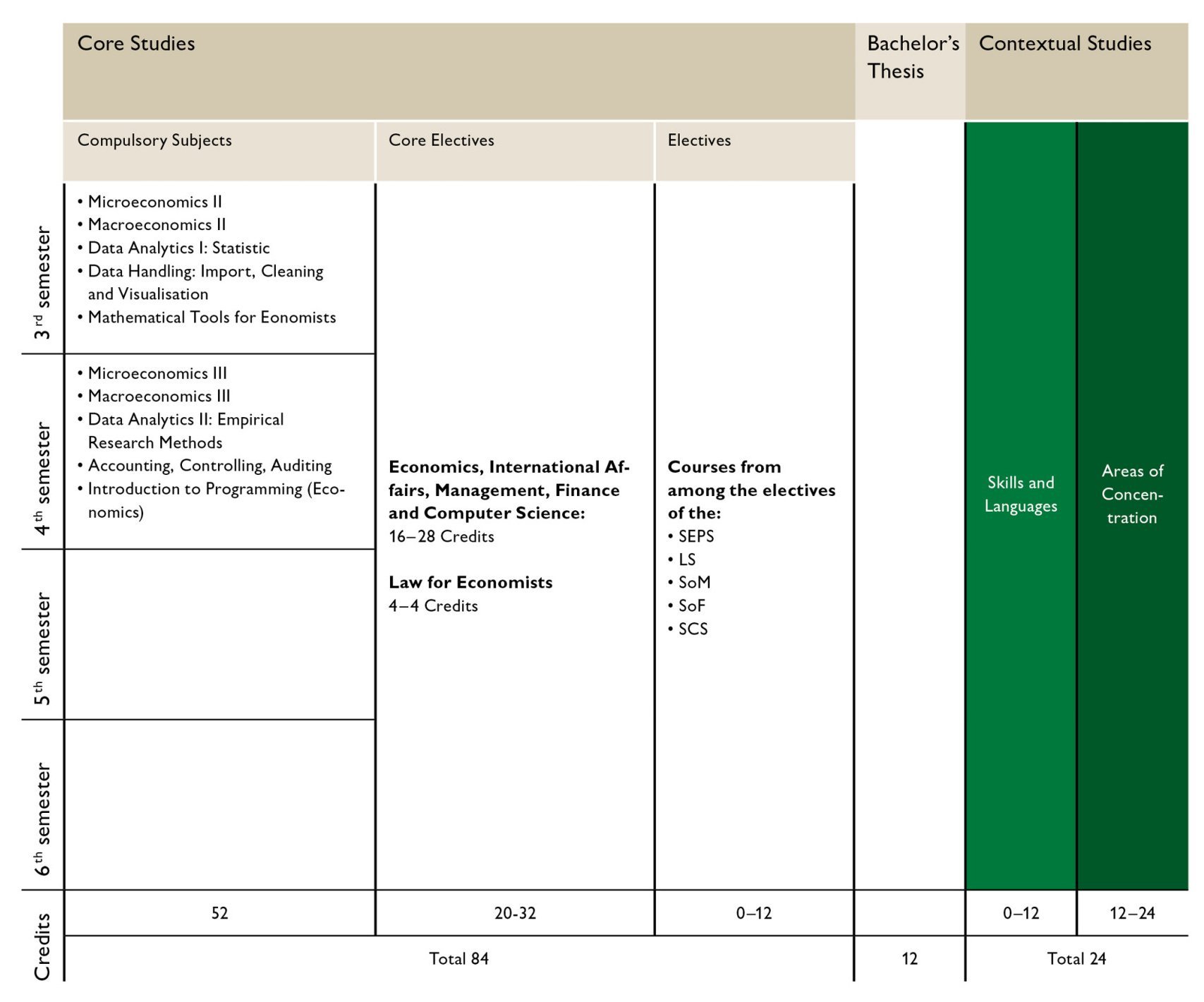
After successful completion of the Assessment Year, you will deepen your knowledge of economics in the Major Economics The degree programme is divided into three parts: Compulsory Pillar, Core Electives and Electives Pillar.
As a full-time programme, the Major Economics is designed for a standard period of study of four semesters. The study period can be extended to a maximum of ten semesters. You will earn a total of 120 ECTS credits.
Do you want to study the Major Economics in German or English? You can decide for yourself by choosing the respective courses, although some of the compulsory courses are only offered in English. Which ever way, our students are excellently prepared for a career in German and English-speaking companies or organisations. You must also complete at least 8 ECTS credits in the opposite language.
Foreign languages are important to us. By the time you complete your Bachelor's degree, we require proof of proficiency in two foreign languages (in addition to your school language). You will attend a first foreign language during the Assessment Year, and learn a second foreign language when studying in the chosen Major. The range of foreign language courses offered is broad; in addition to European languages, there are courses in Arabic, Chinese and Japanese at various levels of proficiency.
Your degree programme consists of compulsory subjects, compulsory elective subjects and elective subjects, which we will present separately below. The compulsory subjects give you a clear profile. Over two semesters, you will receive subject- and topic-related training in the core disciplines of economics, methodology courses and basic business administration knowledge, totalling 52 ECTS credits. Thanks to the concentration on the third and fourth semesters, you can freely organise the fifth and sixth semesters according to your own ideas and easily complete an exchange semester. In addition, you will gain valuable insights into current economic issues and learn how to handle large amounts of data.
The compulsory area comprises a total of 10 courses, four in the core disciplines of micro and macroeconomics, four methodology courses and one course on accounting, controlling and auditing.
| Course | ECTS | Dozierende | Language | Semester |
| 3,135 Accounting, Controlling, Auditing | 4 | Prof. PhD. Florian Eugster Prof. Dr. Dennis Fehrenbacher | English | Autumn |
| 3,220 Mikroökonomik II | 4 | Prof. Dr. Stefan Bühler | German | Autumn |
| 3,202 Microeconomics II | 4 | Prof. Dr. Stefan Bühler | English | Autumn |
| 3,210 Makroökonomik II | 4 | Prof. Dr. Winfried Koeniger Jonas Bruhin | German | Autumn |
| 3,212 Macroeconomics II | 4 | Prof. Dr. Winfried Koeniger Dr. Magnus Hoffmann | English | Autumn |
| 3,220 Data Analytics I: Statistik (BVWL) | 6 | Prof. Dr. Tobias Sutter | German | Autumn |
| 3,222 Data Analytics I: Statistics (Economics) | 6 | Prof. PhD. Francesco Audrino | English | Autumn |
| 3,230 Data Handling: Import, Cleaning and Visualisation | 4 | Dr. Aurélien Sallin | English | Autumn |
| 3,232 Mathematical Tools for Economists | 6 | Prof. Dr. Paolo Giovanni Piacquadio | English | Autumn |
| 4,135 Accounting Controlling, Auditing | 4 | Prof. Dr. Peter Leibfried Prof. Dr. Matthias Mitterlechner | German | Spring |
| 4,200 Mikroökononik III | 6 | Prof. Ph.D. Michèle Müller-Itten | German | Spring |
| 4,202 Microeconomics III | 6 | Prof. Ph.D. Michèle Müller-Itten | English | Spring |
| 4,212 Macroeconomics III | 6 | Prof. Guido Cozzi | English | Spring |
| 4,220 Data Analytics II: Empirical Research Methods | 6 | Prof. Ph.D. Beatrix Eugster Prof. Dr. Johanna Kutz | English | Spring |
| 4,222 Introduction to Programming (Economics) | 6 | Dr. Aurélien Sallin Franziska Bender | English | Spring |
You can find the current course offerings and the respective course descriptions in the online course catalogue. The course descriptions contain further information such as topics, structure and examination format for each course.
Building on the solid foundation of the compulsory area, you can further refine your study profile, deepen your individual interests and thus broaden your economic perspective within the compulsory elective area.
You can choose between 20-32 ECTS credits in compulsory elective courses, which are composed of the compulsory elective area of economics, international affairs, management, finance and computer science (16-28 ECTS credits) and the compulsory elective area of law for economists (4 ECTS credits). The compulsory elective area enables students to deepen and expand their knowledge in the core disciplines of the compulsory area and/or combine it with other courses.
In the elective area, you have the opportunity to attend courses with other thematic focuses.
The following courses are currently offered in the compulsory elective area of econometrics, international affairs, management, finance and computer science:
| Courses offered | Programm | ECTS | Semester |
| 3,130 Corporate Finance (BBWL) | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 3,318 Intergenerational Fairness | BIA | 4 | Autumn |
| 3,585 Applied Monte Carlo Simulation in R | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,108 Business Analytics and Data Science Applications | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,111 Fundamentals of Cybersecurity | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,115 Asset-backed Commodity Trading | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,117 Real Estate Finance and Investments | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,120 Designing Digital Business Models | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,124 Financial Statement Analysis and Corporate Valuation | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,127 Management in the Digital Economy | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,129 Blockchain and Money | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,139 Strategic Foresight | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,149 Equity Investing and Fundamental Analysis | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,152 Risk Management | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,153 Dealing with Uncertainty in Dynamic Markets | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,155 Machine Learing in Finance | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,240 Game Theory and Applications | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,241 Prompt Engineering for Economists | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,242 International Economics (VWL) | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,244 Economic History | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,250 Declining Business Dynamism: Drivers and Consequences | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,251 Data Analytics: Statistical Programming | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,252 Stadtökonomie | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,253 Optimal Decision Making | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,256 Public Policy Evaluation: Theory, Tools, and Applications | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,258 Introduction to Environmental Economics | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,262 Public Economics: Public Policy | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,263 Behavioral and Experimental Economics | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,267 Ökonomie des Glücks | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,268 Behavioral Macroeconomics | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,910 Coding wit AI | BCS | 3 | Autumn |
| 4,130 Corporate Finance (BBWL) | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 4,309 The Politics of Climate Change | BIA | 4 | Spring |
| 4,583 Mathematical Tools for Data Science | DSF | 4 | Spring |
| 6,100 Business and Market Research | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,121 Data-driven Service Design and Management | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,124 International Accounting from the Perspective of a CFO | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,138 Strategies and Business Practices of Swiss Global SMEs | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,140 Asset-backed Commodity Trading | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,141 Principles of Financial and Actuarial Mathematics | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,142 Applied Corporate Valuation (BBWL) | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,143 Investments | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,155 Machine Learning in Finance | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,156 Introduction to Financial Derivatives | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,244 Introduction to Market Design | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,246 Monetary Economics | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,250 Democratic Choice and Social Welfare | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,252 Stochastic Methods in Finance | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,258 Evaluation of Labour Policy | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,264 Introduction to Normative Economics | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,268 Wettbewerbspolitik: Theorie und Praxis | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,270 Time Series Analysis | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,271 Financial Econometrics | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,272 Money, Banking and Finance | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,274 Database Fundamentals for Data Science | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,305 Introduction to Fixed-Income Markets | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,306 Business and Politics: A risk Perspective | BIA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,318 Economics of Climate Change | BIA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,902 Introduction to Big Data Analytics | BCS | 3 | Spring |
| 6,912 Financial Time Series in Python | BCS | 3 | Spring |
The current course offerings and descriptions can be found in the online course catalogue. The course descriptions contain further information such as topics, structure and examination format for each course.
Please note that the course offerings correspond to the current planning status.
Building on the solid foundation of the Compulsory courses, you can sharpen your study profile, deepen your individual interests and broaden your Economic perspective with courses offered in the Core Electives Pillar.
You can choose between 20-32 ECTS credits of Core Electives Pillar are which are made up of the Core Electives Economics, International Affairs, Management, Finance and Computer Science (16-28 ECTS credits) and the Core Electives Law for Economists (4 ECTS credits). The Core Electives enables students to deepen and broaden their knowledge in the core disciplines of the compulsory area and/or combine it with other courses.
In the Electives Pillar, you have the opportunity to attend courses focussing on other topics.
The following courses are currently offered in theCore Electives Law for Economists:
| Offered courses | Programme | ECTS | Semester |
| 3,145 Business and Tax Law | BBA | 8 (only 4 can be credited) | Autumn |
| 3,324 European Law | BIA | 4 | Autumn |
| 3,512 Integrative Course International Trade Law & Policy | BLE | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,248 Economic Incentives and the Law: A Decision-Theoretic Approach | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,265 Climate Law and Policy | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,300 International Law | BIA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,415 Völkerrecht | BLaw | 4 | Autumn |
| 4,145 Wirtschafts- und Steuerrecht | BBA | 8 (only 4 can be credited) | Spring |
| 4,314 European Law | BIA | 4 | Spring |
In the Online Course Directory you can find the entire course offering and the course factsheets. In the respective course factsheet you will find more information on the topic, structure and exam type.
Please note that the range of courses corresponds to the current planning status.
In the Electives Pillar (0-12 ECTS credits), you can choose from a wide range of courses from the other Majors. This allows you to organise your studies according to your individual preferences - either through a broad portfolio of courses or by focusing on courses in a specific subject area.
In the Online Course Directory you can find the entire course offering and the course factsheets. In the respective course factsheet you will find more information on the topic, structure and exam type.
Please note that the range of courses corresponds to the current planning status.
Do you want to give your degree programme a profile to communicate it to future employers? In the Major Economics, you can voluntarily choose a specialisation relevant to your degree. This will be shown on your final transcript.
The voluntary specialisationsare geared towards the different interests of the students and further sharpen the labour market profile. A voluntary specialisation can be chosen in one of the following areas:
In order to complete the Major Economics with one of the above voluntary specialisations, you must complete at least 16 ECTS credits from a defined list of courses and write your Bachelor's Thesis in the corresponding subject area. You must clarify in advance with the programme management of the Major Economics whether the topic you choose for your bachelor's thesis is relevant to the specialisation in terms of its content.
You can find the current range of courses for the voluntary specialisations in the Online Course Directory.
The Bachelor's Thesis (12 ECTS credits) is an academic research paper. The topic of the Bachelor's Thesis should be related to one or more subject areas of the Economics degree programme. In the Bachelor's Thesis, you will be guided by the relevant scientific research designs and principles.
Thesis Preparation Colloquium
The «Thesis Preparation Colloquium» is designed to promote academic maturity in relation to student research. The main objective of this Colloquium is to enable students to design, develop, conduct and document independent scientific research projects. The Colloquium is intended to support students in the preparation of their Bachelor's Thesis.
During the Colloquium, students have the opportunity to improve their research question and discuss a suitable research design.
The Colloquium is offered in the Autumn and Spring. Attendance is compulsory and it is recommended to complete the course towards the end of the degree programme, but before registering for the Bachelor's Thesis. The Colloquium is not graded.
Internationalisation and intercultural exchange are important topics in the Major Economics. Many of our students are drawn to one of our partner University worldwide in their fifth or sixth semester. We very much welcome you spending an exchange semester either at one of our partner Universities or at a University of your choice. You can also gain up to 32 ECTS credits abroad and, above all, acquire intercultural skills without having to interrupt your studies.
Here you will find a summary of the most important legal provisions in the Bachelor's degree programme.
Digitalisation and the abundance of data are changing the world. Companies are reinventing their business models, global trade is shifting online, and governments are finding new ways to interact with citizens. How can machine learning and econometrics make data useful? How can companies and governments develop tailored solutions? How is digital trade changing competition? The data-driven future requires new skills.
Employers: Positions that demand comprehensive knowledge of handling large datasets in a digital environment can be found across all sectors of the economy: in private companies, consulting firms, government and research institutions, as well as in the financial industry. The competent analysis of big data and digital transformation also provide many current research topics for a dissertation.
To complete the Major Economics with the designated specialisation in «Economic Data Science», you must earn at least 16 ECTS credits from the courses listed below and write your Bachelor’s Thesis in the field of «Economic Data Science».
Whether the chosen Thesis topic can be classified under this specialisation must be clarified in advance with the Programme Management of the Major Economics.
| Course | Programme | ECTS | Semester |
| 3,585 Applied Monte Carlo Simulation in R | DSF | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,108 Business Analytics und Data Science Applications | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,111 Fundamentals of Cybersecurity | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,135 Introduction to Human-Computer Interaction | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,241 Prompt Engineering for Economists | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,251 Data Analytics: Statistical Programming | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,253 Optimal Decision Making | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,910 Coding with AI | BCS | 3 | Autumn |
| 4,583 Mathematical Tools for Data Science | DSF | 4 | Spring |
| 6,121 Data-driven Service Design and Management | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,155 Machine Learning in Finance | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,252 Stochastic Methods in Finance | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,270 Time Series Analysis | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,171 Financial Econometrics | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,274 Database Fundamentals for Data Science | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,902 Introduction to Big Data Infrastructures | BCS | 3 | Spring |
| 6,912 Financial Time Series in Python | BCS | 3 | Spring |
The course offerings may vary by semester, as not all courses are available every semester. Please refer to the current course catalogue for up-to-date information. This table serves as a guide. The Programme Management strives to update the list for each semester and to offer sufficient courses for each voluntary specialisation.
You can find more information in the current course listings at courses.unisg.ch.
«The Science of Sustainability»: Economics focuses on the efficient use of scarce resources within a society and is also referred to as "Economics" or "Ökonomie," derived from the Greek word «Oikos» meaning family or household.
Whether in a team, a company, or the economy as a whole, our resources for producing goods and services are limited. This raises two fundamental questions: How can a certain output be achieved with the least possible use of resources? And how can an ideal outcome be attained with a given set of resources? In the study of economics, these are two central questions, and one learns how a society can and should manage limited resources—labour, capital, nature, and time—sustainably.
Business Economics is an area of applied economics that deals with the financial, organisational, market-related, and environmental issues faced by companies. It covers topics such as the concept of scarcity, production factors, distribution, and consumption.
To complete the Major Economics with the designated specialisation in «Business Economics», you must earn at least 16 ECTS credits from the courses listed below and write your Bachelor’s Thesis in the field of «Business Economics».
Whether the chosen Thesis topic can be classified under this specialisation must be clarified in advance with the Programme Management of the Major Economics.
| Course | Programme | ECTS | Semester |
| 3,130 Corporate Finance (BBWL) | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,115 Asset-backed Commodity Trading | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,117 Real Estate Finance and Investments | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,120 Designing Digital Business Models | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,127 Management in the Digital Economy | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,129 Blockchain and Money | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,139 Strategic Foresight | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,149 Equity Investing and Fundamentals Analysis | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,152 Risk Management | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,153 Dealing with Uncertainty in Dynamic Markets | BBA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,240 Game Theory and Applications | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,250 Declining Business Dynamism: Drivers and Consequences | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,267 Ökonomie des Glücks | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 4,130 Corporate Finance (BBWL) | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,100 Business and Market Research | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,124 International Accounting from the Perspective of the CFO | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,138 Strategies and Business Practices of Swiss Global SMEs | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,141 Principles of Financial and Actuarial Mathematics | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,142 Applied Corporate Valuation (BBWL) | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,143 Investments | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,151 Financial Statement Analysis and Corporate Valuation | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,156 Introduction to Financial Derivatives | BBA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,244 Introduction to Market Design | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,268 Wettbewerbspolitik: Theorie und Praxis | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,272 Money, Banking and Finance | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,305 Introduction to Fixed-Income Markets | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,306 Business and Politics: A Risk Perspective | BIA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,318 Economics of Climate Change | BIA | 4 | Spring |
The course offerings may vary by semester, as not all courses are available every semester. Please refer to the current course catalogue for up-to-date information. This table serves as a guide. The programme management strives to update the list for each semester and to offer sufficient courses for each voluntary specialisation.
You can find more information in the current course listings at courses.unisg.ch.
«Economic Policy» offers timely and well-founded analyses of the decisions faced by policymakers. The range of topics spans from examining how individual markets can and should function to the broader interactions within the global economy. «Business Economics».
With a focus on the relationship between the state and the economy, economic policy addresses situations where government intervention is necessary, explores what options are available, and defines where the limits lie. When should the state implement regulatory measures to help the economy reach its full potential—and which measures should be taken?
Economic policy pursues a range of different goals and topics, which sometimes move in opposing directions—it addresses issues of stability, growth, the government’s provision of public goods, competition, and distributive justice. Other important aspects include the institutional framework in which economic policy decisions are made and the ability to empirically assess the effectiveness of political measures.
Through this specialisation, you will acquire valuable economic policy knowledge, which is highly sought after in organisations such as central banks, economic media, and international institutions.
To complete the Major Economics with the designated specialisation in «Economic Policy», you must earn at least 16 ECTS credits from the courses listed below and write your Bachelor's Thesis in the field of «Economic Policy»
Whether the chosen Thesis topic can be classified under this specialisation must be clarified in advance with the Programme Management of the Major Economics.
| Course | Programme | ECTS | Semester |
| 3,318 Intergenerational Fairness | BIA | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,242 Economic Incentives and the Law: A Decision-Theoretic Approach | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,252 Stadtökonomie | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,256 Public Policy Evaluation: Theory, Tools, and Applications | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,258 Introduction to Environmental Economics | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,262 Public Economics: Public Policy | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 5,268 Behavioral Macroeconomics | BEcon | 4 | Autumn |
| 4,309 The Politics of Climate Change | BIA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,246 Monetary Economics | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,250 Democratic Choice and Social Welfare | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,258 Evaluation of Labour Policy | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,264 Introduction to Normative Economics | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,268 Wettbewerbspolitik: Theorie und Praxis | BEcon | 4 | Spring |
| 6,306 Business and Politics: A Risk Perspective | BIA | 4 | Spring |
| 6,318 Economics of Climate Change | BIA | 4 | Spring |
The course offerings may vary by semester, as not all courses are available every semester. Please refer to the current course catalogue for up-to-date information. This table serves as a guide. The Programme Management strives to update the list for each semester and to offer sufficient courses for each voluntary specialisation.
You can find more information in the current course listings at courses.unisg.ch.
The Contextual Studies is another unique feature of the University of St.Gallen (HSG). It integrates knowledge across disciplines and strengthens the social and cultural competencies of our students distinctively. Students take a holistic approach by "thinking outside the box" and enrol in courses within focus areas and skills areas. The cultural and social science offerings in the focus areas are highly diverse and aligned with the study programme. In the skills area, students acquire additional competencies and practical skills necessary for success in the business world, e.g. presentation and negotiation techniques or programming. The Contextual Studies complements your main field of study and is awarded with 24 ECTS credits.
learn more about the Contextual Studies